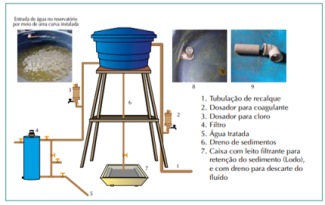
Description
SALTA-z is a water treatment solution developed by technicians from the National Health Foundation (Funasa) and aimed at serving small communities, which do not have access to potable water, where the available raw water has high iron, manganese or turbidity levels.
The Simplified Collective Alternative Solution for Water Treatment (SALTA-z, acronym in Portuguese) provides a solution for communities without access to potable water. The history of its implementation, through technical cooperation between Funasa and municipalities, has shown positive results in improving the health of the beneficiary populations..
Funasa donates this social technology and provides for training of municipal technicians and local operators, in order to promote the quality of drinking water, within the potability standards recommended by current legislation, stimulating the development of healthy environments and the empowerment of the communities served.
Number of infrastructures installed from 2017 to 2021
2017: 2 units
2018: 178 units
2019: 361 units
2020: 85 units
2021: 37 units - 442 municipalities served
(Source: Funasa Management Report, 2021)
Criteria 11/11
- ACCESSIBILITY
- ALIGNMENT WITH SDG 1,3,4,6 AND/OR 11
- RACE AND GENDER ISSUES
- ATTENTION TO CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
- LOW COST
- SOCIAL DIFFUSION
- ADMINISTRATIVE EFFICIENCY
- ADHERENCE AND CONTINUITY AT LOCAL LEVEL
- WASH INITIATIVE
- CLIMATE RESILIENCE
- SUSTAINABILITY
Implemented in collaboration with the municipal management of each municipality to implement and support the monitoring of the solution. Water quality standards must adhere to the parameters set by the Health Regulatory Secretariat (SVS) of the Ministry of Health.
SALTA-z is a technology that was developed in order to favor
access to potable water for rural and traditional populations, or of special interest to the federal government, that lack access to other source of safe water and are therefore more vulnerable to water-related diseases. SALTA-Z is adapted to the environments and serves riverside, quilombola and indigenous communities.
More than 600 communities served from 2017 to 2021 at the national level.
Quantitative of the population served per State (2017 to 2021)
Acre - 185
Amapá - 8,261
Amazonas - 26,149
Pará - 73,357
Rondônia - 7,984
Roraima - 6,828
Tocantins - 2,730
Alagoas - 857
Bahia - 1,243
Ceará - 1,170
Maranhão - 915
Paraíba - 3,415
Piauí - 1,650
Rio Grande do Norte - 1,615
Paraná - 73
Rio Grande do Sul - 859
Santa Catarina - 7,740
Minas Gerais - 2,372
Rio de Janeiro - 1,347
Mato Grosso - 530
(Source: Funasa Management Report, 2021)
Since 2017
It involves the completion of a Technical Cooperation Agreement (ACT) between Funasa and the municipal government. To implement the ACT, it is necessary to meet specific conditions, commit to supporting infrastructure construction, monitor progress, and carry out community engagement activities.
The clauses established in the Technical Cooperation Agreement provide for the definitive donation of the equipment, with a systematized knowledge transfer process, aiming at the autonomy of the community involving the leaders and the population itself.
The SALTA-z project begins with the municipality expressing interest through mobilization meetings, followed by the formal submission of a request for infrastructure and training workshops to Funasa.
The municipality must prepare an Action Plan to implement SALTA-z containing, at least, a description and schedule of the activities, responsible servers and costs.
The SALTA-Z project includes a methodology that involves conducting a multiplier training workshop to equip technicians with the skills needed for structural actions, water quality maintenance, and environmental health education.
SALTA-z is monitored in accordance with the provisions of the legislation on the potability of drinking water, namely: GM/MS Ordinance No. 888/2021. This ordinance provides guidelines related to the water potability standard for all municipal public supply systems.
It is worth noting that the SALTA-Z project, when passed on to the municipality, is required in the Funasa Service Order to be monitored by the local city hall, based on the aforementioned legislation.
The resources for implementing SALTA-Z are provided by Funasa, at no cost to municipalities and communities. The infrastructure for each SALTA-Z unit has an average cost of around 22 thousand reais.
A Technical Cooperation Agreement (ACT) must be established between Funasa and the bidder, which will include a donation term for the equipment. Following this, the process of implementing the technology in the requesting community will begin, along with the training of municipal teams to train multipliers. The implementation must adhere to the manual for the simplified collective alternative solution for water treatment in small communities, using a filter and doser developed by Funasa.